Apr 14, 2006
Emotional Social Intelligence Prosthetic
Via Wired
Wired reports that MIT researchers are developing a wearable computer with a computational model of "mind-reading".

The prosthetic device should be able to infer affective-cognitive mental states from head and facial displays of people in real time, and communicate these inferences to the wearer via sound and/or tactile feedback.
According to MIT researchers, the system could help people afflicted by autism (who lack the ability to ascertain others' emotional status) in doing the "mind reading". A broader motivation of the project is to explore the role of technology in promoting social-emotional intelligence of people and to understand more about how social-emotional skills interact with learning.
A prototype of ESIP was unveiled at at the Body Sensor Networks 2006 international workshop at MIT's Media Lab last week. The video cameras captured facial expressions and head movements, then fed the information to a desktop computer that analyzed the data and gave real-time estimates of the individuals' mental states, in the form of color-coded graphs.
19:20 Posted in Brain training & cognitive enhancement | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 13, 2006
PervasiveHealth 2006
Call for Papers
PervasiveHealth Conference 2006
Inssbruck, Austria, November 29th - December 1st 2006.
www.pervasivehealth.org
Sponsored by:
-IEEE EMB Society,
-ACM Association for Computing Machinery
-CREATE-NET Center for REsearch And Telecommunication Experimentation for NETworked communities,
-ICST International Communication Sciences and Technology Association
Pervasive healthcare may be defined from two perspectives. First, it is the development and application of pervasive computing (or ubiquitous computing, ambient intelligence) technologies for healthcare, health and wellness management. Second, it seeks to make healthcare available to anyone, anytime, and anywhere by removing locational, time and other restraints while increasing both the coverage and quality of healthcare.
Topics of Interest:
- Design and use of bio-sensors
- Mobile devices for patient monitoring
- Wireless and wear-able devices for pervasive healthcare -Patient monitoring in diverse environments (indoor, outdoor, hospitals, nursing homes, assisted living) -Continuous vs event-driven monitoring of patients -Using mobile devices for healthcare information storage, update, and transmission -Sensing of vital signs and transmission -Home monitoring for cardiac arrhythmias -Preventative care: Technologies to improve overall health of people one wouldn't normally call "patients"
Technologies "situated in the environment"
- The use of "environmental" technologies such as cameras, interfaces, and sensor networks -Data fusion in pervasive healthcare environment -Managing knowledge in pervasive healthcare -Content-based encoding of medical information - Forming ad hoc wireless networks for enhanced monitoring of patients -Networking support for pervasive healthcare (location tracking, routing, scalable architectures, dependability, and quality of access) - Managing healthcare emergency vehicles and routing -Network support for mobile telemedicine -Ubiquitous health care and monitoring at home -Ubiquitous medical network and appliances in homes or hospitals -Ubiquitous computing support for medical works in hospitals
Medical aspects of pervasive healthcare
-Pervasive healthcare applications
-Specific requirements of vital signs in pervasive healthcare environment -Diversity of patients and their specific requirements -Representation of medical information in pervasive healthcare environment (multimedia, resolution, processing and storage requirements) -Role of medical protocols in pervasive healthcare -Improved delivery of healthcare services -The usability of wireless-based solutions in healthcare -Physiological models for interpreting medical sensor data -Decision support algorithms for sensor analysis
Management of pervasive healthcare
-Security and privacy in pervasive healthcare -Training of healthcare professional for pervasive healthcare -Managing the integration of wireless solutions in pervasive healthcare -Increasing coverage of healthcare services -Legal and regulatory issues in pervasive healthcare -Insurance payments and cost aspects -Role of HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996) in pervasive healthcare
Paper Submissions:
Submissions must follow IEEE's conference style two-column format including figures and references. Conference papers will be published by IEEE and CD proceedings will be distributed during the conference days.
Papers submitted to PERVASIVEHEALTH will consist of 10 pages maximum.
Deadlines
-Paper Submission Deadline: June 15th, 2006
-Acceptance: September 1st, 2005
-Camera Ready: September 14th, 2006
19:10 Posted in Call for papers | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 12, 2006
Neural Interfaces: Chip ramps up neuron-to-computer communication
Via VRoot (From New Scientist):
A specialised microchip that could communicate with thousands of individual brain cells has been developed by European scientists.
The device will help researchers examine the workings of interconnected brain cells, and might one day enable them to develop computers that use live neurons for memory.
The computer chip is capable of receiving signals from more than 16,000 mammalian brain cells, and sending messages back to several hundred cells. Previous neuron-computer interfaces have either connected to far fewer individual neurons, or to groups of neurons clumped together.
22:59 Posted in Brain-computer interface | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Social Network Mnemonics for Teenagers
Nicolas Nova (Pasta and Vinegar) has found an article describing a a curious device: Telebeads: Social Network Mnemonics for Teenagers by Jean-Baptiste Labrune and Wendy Mackay (IDC2006)
From the article:
This article presents the design of Telebeads, a conceptual exploration of mobile mnemonic artefacts. Developed together with five 10-14 year olds across two participatory design sessions, we address the problem of social network massification by allowing teenagers to link individuals or groups with wearable objects such as handmade jewelery. We propose different concepts and scenarios using mixed-reality mobile interactions to augment crafted artefacts and describe a working prototype of a bluetooth luminous ring. We also discuss what such communication appliances may offer in the future with respect to interperception, experience networks and creativity analysis.
The ring addresses two primary functions requested by the teens: providing a physical instantiation of a particular person in a wearable object and allowing direct communication with that person. (…) We have just completed an ejabberd server, running on Linux on a PDA, which will serve as a smaller, but more powerful telebead interface


22:51 Posted in Wearable & mobile | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Computer simulations of the mind
Scientific American Mind has a free online article about computer simulations of the mind. The article analyzes how recent technological advances are narrowing the gap between human brains and circuitry.

22:42 Posted in AI & robotics | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
New BCI shown off at CEBIT
Via New Scientist

Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute in Berlin and Charité, the medical school of Berlin Humboldt University in Germany, have developed and succesfully tested a brain-computer interface, which could provide a way for paralysed patients to operate computers, or for amputees to operate electronically controlled artificial limbs.
The device allows to type messages onto a computer screen by mentally controlling the movement of a cursor. A user must wear a cap containing EEG electrodes, and imagine moving their left or right arm in order to manoeuvre the cursor around.
The device was recently presented at the CeBit electronics fair in Hanover, Germany.
Read full article
22:34 Posted in Brain-computer interface | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 11, 2006
First-person experience and usability of co-located interaction in a projection-based virtual environment
From VRoot
First-person experience and usability of co-located interaction in a projection-based virtual environment
A. Simon
Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Proceedings of the ACM symposium on Virtual reality software and technology, Pages: 23 - 30, 2005;
Large screen projection-based display systems are very often not used by a single user alone, but shared by a small group of people. We have developed an interaction paradigm allowing multiple users to share a virtual environment in a conventional single-view stereoscopic projection-based display system, with each of the users handling the same interface and having a full first-person experience of the environment. Multi-viewpoint images allow the use of spatial interaction techniques for multiple users in a conventional projection-based display.
21:00 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
New book about Ubiquitous Computing
Via Smart Mobs
Jon Lebkowsky (WorldChanging) interviews Adam Greenfield about his new book "Everyware: The Dawning Age of Ubiquitous Computing"
 WorldChanging: So you're actually coming from a user experience perspective in your analysis of ubicomp?
WorldChanging: So you're actually coming from a user experience perspective in your analysis of ubicomp?
Adam Greenfield: That's the genesis of it, yeah. That was the real emotional hook for me, just thinking about people having to configure their toilets and people having to configure their teapots to boil a kettle of tea. And just
taking a direct analogy with the technical systems that are around us now - you know, dropped cellphone calls and the blue screen of death, and everything that we're familiar with from the PC and mobile infrastructure.
WorldChanging: The blue toilet of death! (Laughter.)
Adam Greenfield: Can you imagine? And I think what heightened the sense of urgency was that this stuff was moving beyond prototypes in short order. It was moving toward consumer products, toward the digital home and digital convergence. The products were starting to be packaged and shipped. And still nobody was talking about the nonlinear interactions of network systems in one space all operating at once - it's as if none of the people who were designing them had, not so much thought, but felt what it would be like to sit in the middle of a room where you've got fifteen different technical interfaces around you, and you're responding to all of them at once, and they're all responding to you at once.
A List Apart presents an introduction of Everyware. Free sample sections are available at the Everyware mini site.
20:50 Posted in Pervasive computing | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Acceptability and effectiveness of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy
An exploratory mixed methods study of the acceptability and effectiveness of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for patients with active depression and anxiety in primary care.
BMC Psychiatry. 2006 Apr 7;6(1):14
Authors: Finucaine A, Mercer SW
ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is an 8-week course developed for patients with relapsing depression that integrates mindfulness meditation practices and cognitive theory. Previous studies have demonstrated that non-depressed participants with a history of relapsing depression are protected from relapse by participating in the course. This exploratory study examined the acceptability and effectiveness of MBCT for patients in primary care with active symptoms of depression and anxiety METHODS: 13 patients with recurrent depression or recurrent depression and anxiety were recruited to take part in the study. Semi-structured qualitative interviews were conducted three months after completing the MBCT programme. A framework approach was used to analyse the data. Beck depression inventories (BDI-II) and Beck anxiety inventories (BAI) provided quantitative data and were administered before and three months after the intervention. RESULTS: The qualitative data indicated that mindfulness training was both acceptable and beneficial to the majority of patients. For many of the participants, being in a group was an important normalising and validating experience. However most of the group believed the course was too short and thought that some form of follow up was essential. More than half the patients continued to apply mindfulness techniques three months after the course had ended. A minority of patients continued to experience significant levels of psychological distress, particularly anxiety. Statistically significant reductions in mean depression and anxiety scores were observed; the mean pre-course depression score was 35.7 and post-course score was 17.8 (p=0.001). A similar reduction was noted for anxiety with a mean pre-course anxiety score of 32.0 and mean post course score of 20.5 (p=0.039). Overall 8/11 (72%) patients showed improvements in BDI and 7/11 (63%) patients showed improvements in BAI. In general the results of the qualitative analysis agreed well with the quantitative changes in depression and anxiety reported. CONCLUSIONS: The results of this exploratory mixed methods study suggest that mindfulness based cognitive therapy may have a role to play in treating active depression and anxiety in primary care.
20:39 Posted in Meditation & brain | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
A comparison of common spatial patterns in a four-class BCI experiment
A comparison of common spatial patterns with complex band power features in a four-class BCI experiment.
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2006 Apr;53(4):642-51
Authors: Townsend G, Graimann B, Pfurtscheller G
We report on the offline analysis of four-class brain-computer interface (BCI) data recordings. Although the analysis is done within defined time windows (cue-based BCI), our goal is to work toward an approach which classifies on-going electroencephalogram (EEG) signals without the use of such windows (un-cued BCI). To that end, we provide some elements of that analysis related to timing issues that will become important as we pursue this goal in the future. A new set of features called complex band power (CBP) features which make explicit use of phase are introduced and are shown to produce good results. As reference methods we used traditional band power features and the method of common spatial patterns. We consider also for the first time in the context of a four-class problem the issue of variability of the features over time and how much data is required to give good classification results. We do this in a practical way where training data precedes testing data in time.
20:38 Posted in Brain-computer interface | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 10, 2006
Linux devices: Emotional lamp
Via Linux devices
The "emotional lamp," is a WiFi-connected device that can be programmed to respond to real-world events by emanating sequences of gentle color.
 Unlike a telephone or television, the lamp presents information without making intrusive or extensive time demands. Messages and information are diffused subtly into the general ambient, communicated through "color changes and their rate/rhythm of posting."
Unlike a telephone or television, the lamp presents information without making intrusive or extensive time demands. Messages and information are diffused subtly into the general ambient, communicated through "color changes and their rate/rhythm of posting."
Customizable, built-in functions include multi-day weather forecasts, stock market monitoring, traffic conditions on a daily commute route, receipt of a large number of emails or email from an important person, or Web site updates containing specified key words. Additional built-in functions are planned.
Personalization features enable the creation of "bouquets" of friends authorized to interact with the Dal lamp through email, SMS, a Dal lamp of their own, or a telephone gateway service maintained by Violet. From the Violet Website: "The messages are colored animations that can be created for each type of emotion you want to show. A personal language and grammar can be created between two persons: only they know what the lamp is expressing."
The Dal lamp has been exhibited at some of the world's most prestigious museums, including the Centre Pompidou in Paris and The City of Science and Industry in Seoul, Korea. It received the "Star of the Observeur de design, 2004," a design award from the French Agency for the Promotion of Industrial Creations.
17:40 Posted in Emotional computing | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 09, 2006
VRoot: OpenEyes
Via VRoot
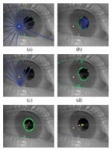 openEyes is an open-source open-hardware toolkit for low-cost real-time eye tracking.
openEyes is an open-source open-hardware toolkit for low-cost real-time eye tracking.
Given the increasing demands for more intuitive computer interfaces, tracking the eye movements of users, which precisely indicates users’ attention states, provides researchers and usability experts with invaluable data. However, the high cost of eye-tracking hardware and the lack of available software that implements long-established eye-tracking methods prohibit many interface developers and researchers from accessing or utilizing critical eye-movement data. In response to the need for more widely accessible eye-tracking hardware and software, Derrick Parkhurst, assistant professor of psychology and associate director of VRAC, created the first open source toolkit for low-cost eye tracking, known as openEyes.
20:39 Posted in Research tools | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
IEEE: Tangible Interaction in Collaborative Environments
26 June 2006 to 28 June 2006
International IEEE Workshop on Tangible Interaction in Collaborative Environments (TICE) at WETICE-2006
June 26 - June 28, 2006
The University of Manchester, Manchester, U.K.
Web site: http://wetice.co.umist.ac.uk/
OVERVIEW
--------
Motivated by these developments, we see this workshop as an opportunity for exploring the potentials and perspectives of tangible interaction for supporting collaborative work. Because of its interdisciplinary topic, TICE 2006 aims at bringing together researchers of various fields, including Human Computer Interaction, Tangible User Interfaces, Computer Supported Collaborative Work, Sociology, Communication Technologies, Embedded Systems and Ubiquitous Computing, to discuss key issues, approaches, open problems, innovative applications, and trends of tangible interaction in collaborative environments.
TOPICS
------
We welcome participants from all disciplines related to the topic of this workshop, including but not limited to Tangible User Interfaces, CSCW and Ubiquitous Computing environments. We invite original research papers and experience reports in all areas of collaborative methods and systems development. Additionally, position papers outlining novel research domains and approaches are welcome. Topics of interest include but are not limited to:
Interaction design of collaborative tangible environments
* Design process for embodied/tangible interaction
* Guidelines, methods and methodologies for collaborative interaction design
* Concepts and patterns for physical and tangible interaction
* Programming paradigms for building tangible environments
* New paradigms for collaborative environments
Technological aspects of tangible user interfaces
* Middleware, platforms and tools
* Architectural concepts for enhancing tangible interaction in groups
* Enabling technologies for instrumenting tangible artefacts
* Innovative technological solutions
Case studies and application scenarios
* Usability studies and evaluations of collaborative tangible environments
* Visions and application scenarios
* Security, privacy and trust in collaborative tangible environments
* Collaborative tangible interaction for mobile users
CO-CHAIRS
---------
Alois Ferscha
Department of Pervasive Computing
Johannes Kepler University Linz
Altenberger Straße 69
4040 Linz, Austria
Web: http://www.pervasive.jku.at/About_Us/Staff/Ferscha
20:33 Posted in Positive Technology events | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Road-crossing safety in virtual reality
Road-crossing safety in virtual reality: a comparison of adolescents with and without ADHD.
J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2006 Jun;35(2):203-15
Authors: Clancy TA, Rucklidge JJ, Owen D
20:29 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Cognews: navigation skills used in robots
From Cognews
How does the ant, without maps and satellite naviation, make regular trips home without getting lost? Dr Markus Knaden, from the University of Zurich, reports that a visit back to the nest is essential for ants to reset their navigation equipment and avoid getting lost on foraging trips. "Knowledge about path integration and landmark learning gained from our experiments with ants has already been incorporated in autonomous robots. Including a 'reset' of the path integrator at a significant position could make the orientation of the robot even more reliable", says Dr Knaden who spoke on Tuesday 4th April at the Society for Experimental Biology's Main Annual Meeting in Canterbury, Kent. ...
20:24 Posted in AI & robotics | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 07, 2006
Wearable vibrotactile systems for virtual contact and information display
Wearable vibrotactile systems for virtual contact and information display
R.W. Lindeman, Y. Yanagida, H. Noma and K. Hosaka
Virtual Reality Volume 9, Numbers 2-3; Date: March 2006; Pages: 203 - 213
This paper presents a development history of a wearable, scalable vibrotactile stimulus delivery system. This history has followed a path from desktop-based, fully wired systems, through hybrid approaches consisting of a wireless connection from the host computer to a body-worn control box and wires to each tactor, to a completely wireless system employing Bluetooth technology to connect directly from the host to each individual tactor unit.
11:16 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Subjective performance in VR
Subjective performance
K. Bormann
Virtual Reality Volume 9, Number 4; Date: April 2006; Pages: 226 - 233
Much effort has gone into exploring the concept of presence in virtual environments. One of the reasons for this is the possible link between presence and performance, which has also received a fair amount of attention. However, the performance side of this equation has been largely ignored.
11:15 Posted in Telepresence & virtual presence | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Supporting visually impaired children with software agents in a multimodal learning environment
Supporting visually impaired children with software agents in a multimodal learning environment
R. Saarinen, J. Järvi, R. Raisamo, E. Tuominen, M. Kangassalo, K. Peltola and J. Salo
Virtual Reality; Volume 9, Numbers 2-3; Date: March 2006; Pages: 108 - 117
11:06 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
1st Annual Serious Games Showcase
11:05 Posted in Serious games | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: serious gaming
Cave Writing Workshop
From the CAVE Writing website
The Cave Writing Workshop is an advanced experimental electronic writing workshop, exploring the potential of text, sound, and narrative movement in immersive three-dimensional virtual reality. It brings together teams of undergraduate and graduate fiction writers, poets and playwrights, composers and sound engineers, graphic designers, visual artists, 3D modelers and programmers, to develop, within the environment of Brown’s “Cave” in the Technology Center for Advanced Scientific Computing and Visualization, projects that focus on the word.

Powered by a high-performance parallel computer, the Cave is an eight-foot cube, wherein the floor and three walls are projected with high-resolution stereo graphics to create a virtual environment, viewed through special “shutter-lens” glasses. The Cave Writing Workshop has introduced a Macintosh sound server to provide positional sound and augment the Cave’s performance potential, surrounding the “reader” with dynamic three-dimensional sound as well as visuals. It has brought text into this highly visual environment in the composing of narrative and poetic works of art, and has experimented with navigational structures more akin to narrative, and in particular hypertext narrative, than to the predominant forms of spatial exploration.
11:04 Posted in Cyberart | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology






