May 14, 2006
South Korea develops next wave of virtual reality goggles
Via VRoot

Kowon Technology said the product would provide consumers with crystal clear video images alongside high-quality audio sounds that would be enjoyed privately through two liquid crystal display panels (LCD).
Read the full story on Yahoo! News
14:45 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
May 13, 2006
Spontaneous mentalizing during an interactive real world task: An fMRI study
Spontaneous mentalizing during an interactive real world task: An fMRI study.
Neuropsychologia. 2006 May 8;
Authors: Spiers HJ, Maguire EA
There are moments in everyday life when we need to consider the thoughts and intentions of other individuals in order to act in a socially appropriate manner. Most of this mentalizing occurs spontaneously as we go about our business in the complexity of the real world. As such, studying the neural basis of spontaneous mentalizing has been virtually impossible. Here we devised a means to achieve this by employing a unique combination of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a detailed and interactive virtual reality simulation of a bustling familiar city, and a retrospective verbal report protocol. We were able to provide insights into the content of spontaneous mentalizing events and identify the brain regions that underlie them. We found increased activity in a number of regions, namely the right posterior superior temporal sulcus, the medial prefrontal cortex and the right temporal pole associated with spontaneous mentalizing. Furthermore, we observed the right posterior superior temporal sulcus to be consistently active during several different subtypes of mentalizing events. By contrast, medial prefrontal cortex seemed to be particularly involved in thinking about agents that were visible in the environment. Our findings show that it is possible to investigate the neural basis of mentalizing in a manner closer to its true context, the real world, opening up intriguing possibilities for making comparisons with those who have mentalizing problems.
20:07 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Virtual Reality in Google Trends
Visualizing the usage of the term "Virtual Reality" with the new Google Trends
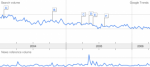
(click here for larger image)
20:02 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
World's Largest 3D-Display

From Networked Performance:
"Electrical engineering students at the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands have created the world's largest 3D-display. The display consists of 8,000 suspended ping pong balls that each contain a red LED light. It play games of 3D snake, 3D pong, and 3D duckhunt, as wll as displaying SMS messages and simple animations"
19:48 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
May 10, 2006
Toward direct biocontrol using surface EMG signals
Toward direct biocontrol using surface EMG signals: Control of finger and wrist joint models.
Med Eng Phys. 2006 May 6;
Authors: Reddy NP, Gupta V
Increased interest in virtual reality (VR) and telemanipulation has created a growing need for the development of new interfacing devices for measuring controlling actions of the human hand. The objective of the present study was to determine if surface electromyography signals (SEMG) from the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS), and flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) generated during flexion-extension of the human index finger and wrist can be used for controlling the flexion-extension of the finger and wrist of a simple geometric computer model. A simple geometric computer model of finger and wrist joints was developed. Eighteen subjects controlled the computer model using the SEMG signals from their FDS and FCU. The results indicate that the SEMG signals from the FDS and FCU muscles can be used as a direct biocontrol technique for controlling the finger and wrist models. This study establishes the proof of concept for direct biological control of the dynamic motion of the finger and wrist models for use in virtual reality environments and telemanipulation.
22:54 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
May 07, 2006
Living with three arms
Via VRoot
(From Virtual Worldlets)
Virtual Reality is just beginning to head down the full body sensation reproduction path. We are at the very early stages of being able to recreate parts of the physical form, entirely in the virtual. This is a concept which is likely to have very a profound effect upon how we deal with the world around us.
At the moment, VR technology in reproducing virtual limbs is limited to a single limb at a time. This is done by mimicking the movements of the user's physical limb by reading the signals sent down the brainstem, translating and implementing them, as opposed to monitoring the movement of the arm and duplicating that. This is both faster than mimicking the movement observationally, and also allows the technique to work if the user has no physical arm to mimic, so long as the brain is capable of controlling one - e.g., quadriplegics, limb amputees.
13:51 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
May 06, 2006
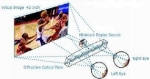
New personal video display device
Via Emerging Technology Trends

The new personal video display device developed by the Israeli company Mirage Innovations Ltd looks like a simple pair of glasses. According to the company, the technology
"is based on the principle of transforming a thin transparent plate into a complete wearable personal display system. The diffractive planar optics is combined with a microdisplay source, such as micro LCD, LCOS or OLED"
One of the most interesting feature of the new display is that it eliminates the dizziness phenomenon usually associated with this kind of display. The product is not currently on the market.
19:05 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
LA Immersive Technologies Enterprise
Via the Presence Mailing List
(From The Acadiana)
Virtual reality is commonly the stuff of science fiction — but the real-world applications made possible by using computer simulations inside a virtual reality environment are as tangible as diapers and oil wells.
The soon-to-open Louisiana Immersive Technologies Enterprise will make any number of research and business applications possible, said Carolina Cruz-Neira, the newly hired chief scientist at LITE.
Cruz-Neira gave an overview of LITE on Thursday at the TechSouth technology summit.
At the heart of LITE is a supercomputer and 6-sided (hexagonal) visual immersion cave. The supercomputer can process and simulate an enormous amount of data, then project that visual data onto the screens of the cave, which serves as a virtual reality environment that allows researchers to better understand that data...
Read the full article
18:58 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 27, 2006
Mobile VR Glasses
From 3pointd.com:

SpatiaLight, which manufactures “ultra high-resolution Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCoS) microdisplays for the high definition television market,” has a press release accouncing that it’s now developing “a 3-D eyeglass-type display device for use with wireless phones, personal digital assistants and personal media players, which enable the viewing of broadband content, cable and satellite television, music videos as well as playing of video games, all with the experience of high definition large screen television.” Imagine: instead of all the laptops at Starbucks, we’ll one day see a bunch of people logging into the virtual world via a hyper-powered Blackberry and their SpatiaLight VR glasses.
23:10 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 18, 2006
VRoot: Polhemus announces new tracker
Polhemus, the industry leader in 6 Degree of Freedom (6DOF) motion capture, tracking and digitizing technologies is proud to announce MINUTEMAN™, the new low cost (under $1,500) 3-Degree-of-Freedom (3DOF) tracking product. MINUTEMAN represents a quantum leap in new technology and state of the art Digital Signal Processor (DSP) electronics which results in a major price reduction for tracking technology. MINUTEMAN is drift free, has the speed of 75 Hz per sensor and offers ease of use via an intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI). The electronics unit (E-Pod), which is powered by the USB interface and contains the electromagnetic source, is only slightly larger than a pack of playing cards. Full InertiaCube2 emulation software is also provided for plug-and-play hardware replacement without having to worry about rewriting code. The combination of all these attributes clearly positions MINUTEMAN as a new class of electromagnetic tracking, offering significant improvements over competitive technologies.
20:20 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Moving while being seated
Via Emerging Technology Trends
Researchers from Max Plank Institute (Germany) and Chalmers University of Technology (Sweden) have developed a new virtual reality prototype, which gives users the illusion of movement while being seated. According to developers, this approach could lead to commercial low-cost VR simulators in the near future.
 The simulator "exploits a vection illusion of the brain, which makes us believe we are moving when actually we are stationary. The same can be experienced, for instance, when you are stopped at a traffic light in your car and the car next to you edges forward. Your brain interprets this peripheral visual information as though you are moving backwards".
The simulator "exploits a vection illusion of the brain, which makes us believe we are moving when actually we are stationary. The same can be experienced, for instance, when you are stopped at a traffic light in your car and the car next to you edges forward. Your brain interprets this peripheral visual information as though you are moving backwards".
More information about the scientific background of this approach can be found in the paper entitled "Influence of Auditory Cues on the Visually Induced Self-Motion Illusion (Circular Vection) in Virtual Reality" (PDF format, 9 pages, 1.22 MB).
The VR system is the main outcome of the EU-funded project POEMS "Perceptually Oriented Ego — Motion Simulation".
10:41 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 11, 2006
First-person experience and usability of co-located interaction in a projection-based virtual environment
From VRoot
First-person experience and usability of co-located interaction in a projection-based virtual environment
A. Simon
Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Proceedings of the ACM symposium on Virtual reality software and technology, Pages: 23 - 30, 2005;
Large screen projection-based display systems are very often not used by a single user alone, but shared by a small group of people. We have developed an interaction paradigm allowing multiple users to share a virtual environment in a conventional single-view stereoscopic projection-based display system, with each of the users handling the same interface and having a full first-person experience of the environment. Multi-viewpoint images allow the use of spatial interaction techniques for multiple users in a conventional projection-based display.
21:00 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 09, 2006
Road-crossing safety in virtual reality
Road-crossing safety in virtual reality: a comparison of adolescents with and without ADHD.
J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2006 Jun;35(2):203-15
Authors: Clancy TA, Rucklidge JJ, Owen D
20:29 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 07, 2006
Wearable vibrotactile systems for virtual contact and information display
Wearable vibrotactile systems for virtual contact and information display
R.W. Lindeman, Y. Yanagida, H. Noma and K. Hosaka
Virtual Reality Volume 9, Numbers 2-3; Date: March 2006; Pages: 203 - 213
This paper presents a development history of a wearable, scalable vibrotactile stimulus delivery system. This history has followed a path from desktop-based, fully wired systems, through hybrid approaches consisting of a wireless connection from the host computer to a body-worn control box and wires to each tactor, to a completely wireless system employing Bluetooth technology to connect directly from the host to each individual tactor unit.
11:16 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Supporting visually impaired children with software agents in a multimodal learning environment
Supporting visually impaired children with software agents in a multimodal learning environment
R. Saarinen, J. Järvi, R. Raisamo, E. Tuominen, M. Kangassalo, K. Peltola and J. Salo
Virtual Reality; Volume 9, Numbers 2-3; Date: March 2006; Pages: 108 - 117
11:06 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Mediated social touch
Mediated social touch: a review of current research and future directions
Antal Haans and Wijnand IJsselsteijn
Virtual Reality. Issue: Volume 9, Numbers 2-3; Date: March 2006; Pages: 149 - 159
Abstract
11:00 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Apr 01, 2006
The contribution of virtual reality to research on sensory feedback in remote control
The contribution of virtual reality to research on sensory feedback in remote control
Robert W. Lindeman, Yasuyuki Yanagida, Haruo Noma and Kenichi Hosaka
Virtual Reality, Volume 9, Number 4; Date: April 2006; Pages: 203 - 213
Here we consider research on the kinds of sensory information most effective as feedback during remote control of machines, and the role of virtual reality and telepresence in that research. We argue that full automation is a distant goal and that remote control deserves continued attention and improvement. Visual feedback to controllers has developed in various ways but autostereoscopic displays have yet to be proven. Haptic force feedback, in both real and virtual settings, has been demonstrated to offer much to the remote control environment and has led to a greater understanding of the kinesthetic and cutaneous components of haptics, and their role in multimodal processes, such as sensory capture and integration. We suggest that many displays using primarily visual feedback would benefit from the addition of haptic information but that much is yet to be learned about optimizing such displays.
22:50 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Mar 25, 2006
The current state of VR
Though the current state of VR technology is ahead of what has been brought to the consumer market thus far, compelling applications still need to be developed - ones that really open up new services and information sources almost as much as the Web has already done," said Jackie Fenn at Gartner.
Virtual Reality had a genuine buzz going for it about 10 years ago, when movies like The Lawnmower Man and Virtuosity were getting the green light, and Nintendo's Virtual Boy game system attempted to bring the so-called artificial world into everyday living. The possibility of complete immersion in a computer-generated environment seemed, for a time, to fire up the public's imagination...
20:05 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Mar 23, 2006
Virtual reality machine gives police hallucinations
From Desmoinesregister
Tom Alex
 Des Moines Police Officer Paul Tieszen stepped onto a city bus and into a world he's only heard about.
Des Moines Police Officer Paul Tieszen stepped onto a city bus and into a world he's only heard about.
"Things flash out of nowhere. Small voices saying, 'Go get your medication.' The bus driver is talking to you normally and all of a sudden he starts calling you 'Your Highness.' Then he becomes part of the hallucination," says Tieszen. "It's a whole busload of children, then it changes to a busload of adults. There's a nurse involved. You see normal things and then all of a sudden someone pulls up next to you and says, 'Get off the bus.' "
The bus wasn't real, but the officer's reactions were. And he quickly got a glimpse of what it's like to suffer from a severe mental illness.
Tieszen's window into the world of hallucinations was provided by a high-tech virtual reality mask that police use to better understand the mentally ill people they come in contact with.
"You are in the role of the individual on the bus," he said, trying to describe the experience. "You are seeing what is in the mind of someone who is like that."
The device is called a virtual hallucination machine. It was introduced to police by Teresa Bomhoff, president of the National Alliance for the Mentally Ill of Greater Des Moines....
Read the full article
20:45 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology
Mar 18, 2006
Virtual clay
Via Transmaterial

Researchers at Buffalo's Virtual Reality Lab have developed a virtual sculpting system that replicates in real time the physical act of sculpting a block of clay. A special glove records the force exerted by the hand in manipulating and shaping a block of clay. Force-feedback, hand position, and speed of fingertip motion are communicated to a computer, where the virtual clay is shaped precisely to the contouring of the actual clay.
13:16 Posted in Virtual worlds | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: Positive Technology






