May 26, 2013
Application of alpha/theta neurofeedback and heart rate variability training to young contemporary dancers: State anxiety and creativity.
Application of alpha/theta neurofeedback and heart rate variability training to young contemporary dancers: State anxiety and creativity.
Int J Psychophysiol. 2013 May 15;
Authors: Gruzelier JH, Thompson T, Redding E, Brandt R, Steffert T
Abstract. As one in a series on the impact of EEG-neurofeedback in the performing arts, we set out to replicate a previous dance study in which alpha/theta (A/T) neurofeedback and heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback enhanced performance in competitive ballroom dancers compared with controls. First year contemporary dance conservatoire students were randomised to the same two psychophysiological interventions or a choreology instruction comparison group or a no-training control group. While there was demonstrable neurofeedback learning, there was no impact of the three interventions on dance performance as assessed by four experts. However, HRV training reduced anxiety and the reduction correlated with improved technique and artistry in performance; the anxiety scale items focussed on autonomic functions, especially cardiovascular activity. In line with the putative impact of hypnogogic training on creativity A/T training increased cognitive creativity with the test of unusual uses, but not insight problems. Methodological and theoretical implications are considered.
19:30 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0)
Apr 20, 2012
Neurofeedback using real-time near-infrared spectroscopy enhances motor imagery related cortical activation
Neurofeedback using real-time near-infrared spectroscopy enhances motor imagery related cortical activation.
PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32234
Authors: Mihara M, Miyai I, Hattori N, Hatakenaka M, Yagura H, Kawano T, Okibayashi M, Danjo N, Ishikawa A, Inoue Y, Kubota K
Abstract. Accumulating evidence indicates that motor imagery and motor execution share common neural networks. Accordingly, mental practices in the form of motor imagery have been implemented in rehabilitation regimes of stroke patients with favorable results. Because direct monitoring of motor imagery is difficult, feedback of cortical activities related to motor imagery (neurofeedback) could help to enhance efficacy of mental practice with motor imagery. To determine the feasibility and efficacy of a real-time neurofeedback system mediated by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), two separate experiments were performed. Experiment 1 was used in five subjects to evaluate whether real-time cortical oxygenated hemoglobin signal feedback during a motor execution task correlated with reference hemoglobin signals computed off-line. Results demonstrated that the NIRS-mediated neurofeedback system reliably detected oxygenated hemoglobin signal changes in real-time. In Experiment 2, 21 subjects performed motor imagery of finger movements with feedback from relevant cortical signals and irrelevant sham signals. Real neurofeedback induced significantly greater activation of the contralateral premotor cortex and greater self-assessment scores for kinesthetic motor imagery compared with sham feedback. These findings suggested the feasibility and potential effectiveness of a NIRS-mediated real-time neurofeedback system on performance of kinesthetic motor imagery. However, these results warrant further clinical trials to determine whether this system could enhance the effects of mental practice in stroke patients.
19:39 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Mental practice & mental simulation | Permalink | Comments (0)
Mar 31, 2012
Neurofeedback for insomnia: a pilot study of Z-score SMR and individualized protocols
Neurofeedback for insomnia: a pilot study of Z-score SMR and individualized protocols.
Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2011 Dec;36(4):251-64
Authors: Hammer BU, Colbert AP, Brown KA, Ilioi EC
Abstract. Insomnia is an epidemic in the US. Neurofeedback (NFB) is a little used, psychophysiological treatment with demonstrated usefulness for treating insomnia. Our objective was to assess whether two distinct Z-Score NFB protocols, a modified sensorimotor (SMR) protocol and a sequential, quantitative EEG (sQEEG)-guided, individually designed (IND) protocol, would alleviate sleep and associated daytime dysfunctions of participants with insomnia. Both protocols used instantaneous Z scores to determine reward condition administered when awake. Twelve adults with insomnia, free of other mental and uncontrolled physical illnesses, were randomly assigned to the SMR or IND group. Eight completed this randomized, parallel group, single-blind study. Both groups received fifteen 20-min sessions of Z-Score NFB. Pre-post assessments included sQEEG, mental health, quality of life, and insomnia status. ANOVA yielded significant post-treatment improvement for the combined group on all primary insomnia scores: Insomnia Severity Index (ISI p<.005), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Inventory (PSQI p<.0001), PSQI Sleep Efficiency (p<.007), and Quality of Life Inventory (p<.02). Binomial tests of baseline EEGs indicated a significant proportion of excessively high levels of Delta and Beta power (p<.001) which were lowered post-treatment (paired z-tests p<.001). Baseline EEGs showed excessive sleepiness and hyperarousal, which improved post-treatment. Both Z-Score NFB groups improved in sleep and daytime functioning. Post-treatment, all participants were normal sleepers. Because there were no significant differences in the findings between the two groups, our future large scale studies will utilize the less burdensome to administer Z-Score SMR protocol.
12:47 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0)
Stress, uncertainty and decision confidence
Stress, uncertainty and decision confidence.
Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2011 Dec;36(4):273-9
Authors: Heereman J, Walla P
Abstract. We successfully manipulated decision confidence in a probabilistic prediction task by means of stress as induced by excessive cognitive demands. In particular, our results indicate that decisions (based on high and low, but not intermediate levels of uncertainty) made under stress (confirmed by skin conductance measures) are associated with increased confidence when outcome probabilities are incompletely known (20% residual uncertainty). A different pattern was found when outcome probabilities were completely known (0% residual uncertainty). Here, stress led to decreased decision confidence when decisions were associated with intermediate levels of uncertainty but had no effect in case of high and low levels of uncertainty. In addition we provide evidence for ambiguity--(understood as implicit-risk) assessment being impaired under stress conditions.
12:46 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0)
Aug 26, 2010
Heart Chamber Orchestra
The Heart Chamber Orchestra consists of classical musicians who use their heartbeats to control a computer composition and visualization environment. To my best knowledge, this is the first example of "group biofeedback".
The musicians are equipped with ECG (electrocardiogram) sensors. A computer monitors and analyzes the state of these 12 hearts in real time. The acquired information is used to compose a musical score with the aid of computer software. It is a living score dependent on the state of the hearts.
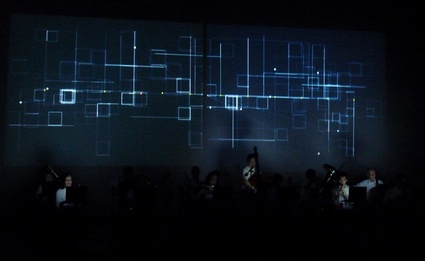

While the musicians are playing, their heartbeats influence and change the composition and vice versa. The musicians and the electronic composition are linked via the hearts in a circular motion, a feedback structure. The emerging music evolves entirely during the performance.
The resulting music is the expression of this process and of an organism forming itself from the circular interplay of the individual musicians and the machine.
The sensor network consists of 12 individual sensors; each one is fitted onto the body of a musician. A computer receives the heartbeat data. Software analyzes the data and generates via different algorithms the real-time musical score for the musicians, the electronic sounds and the computer graphic visualization
Below is a video documentation from the Heart Chamber Orchestra performance on the 28th of March 2010 at Kiasma Theatre at Pixelache Festival in Helsinki, Finland.
20:02 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Creativity and computers, Cyberart | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, heart chamber orchestra, creativity
Dec 20, 2009
Head Chaise: Couching One's Thoughts into a Brain Wave Sofa
From Scientific American
Two European designers, Dries Verbruggen and Lucas Maassen used their alpha waves as a source of inspiration for their design work, which resulted in a piece of furniture, the Brain Wave Couch.
“The process is a wink to a rather futuristic design process,” the couch creators wrote in a press release, “for which a designer merely has to close his or her eyes, or merely rest, to have the brain do all the work, and create the data needed to have the CNC machine cut the shape of the sofa.”
The x-axis of the couch represents Maassen’s brain waves in hertz, while the y-axis shows the amount of alpha activity as a percentage, and the z-axis is the time in milliseconds. Once the foam core of the sofa was completed, the designers covered it by hand in soft gray felt and decorated the valleys of the brain waves with buttons.
The Brainwave Sofa was presented at the Bits ‘n Pieces Exhibition in New York.

20:44 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Creativity and computers | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: brain-computer interface, neurofeedback, creativity
Dec 02, 2009
Neurofeedback Outcomes in Clients with Asperger's Syndrome
Neurofeedback Outcomes in Clients with Asperger's Syndrome.
Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2009 Nov 12;
Authors: Thompson L, Thompson M, Reid A
This paper summarizes data from a review of neurofeedback (NFB) training with 150 clients with Asperger's Syndrome (AS) and 9 clients with Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) seen over a 15 year period (1993-2008) in a clinical setting. The main objective was to investigate whether electroncephalographic (EEG) biofeedback, also called neurofeedback (NFB), made a significant difference in clients diagnosed with AS. An earlier paper (Thompson et al. 2009) reviews the symptoms of AS, highlights research findings and theories concerning this disorder, discusses QEEG patterns in AS (both single and 19-channel), and details a hypothesis, based on functional neuroanatomy, concerning how NFB, often paired with biofeedback (BFB), might produce a change in symptoms. A further aim of the current report is to provide practitioners with a detailed description of the method used to address some of the key symptoms of AS in order to encourage further research and clinical work to refine the use of NFB plus BFB in the treatment of AS. All charts were included for review where there was a diagnosis of AS or ASD and pre- and post-training testing results were available for one or more of the standardized tests used. Clients received 40-60 sessions of NFB, which was combined with training in metacognitive strategies and, for most older adolescent and adult clients, with BFB of respiration, electrodermal response, and, more recently, heart rate variability. For the majority of clients, feedback was contingent on decreasing slow wave activity (usually 3-7 Hz), decreasing beta spindling if it was present (usually between 23 and 35 Hz), and increasing fast wave activity termed sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) (12-15 or 13-15 Hz depending on assessment findings). The most common initial montage was referential placement at the vertex (CZ) for children and at FCz (midway between FZ and CZ) for adults, referenced to the right ear. Metacognitive strategies relevant to social understanding, spatial reasoning, reading comprehension, and math were taught when the feedback indicated that the client was relaxed, calm, and focused. Significant improvements were found on measures of attention (T.O.V.A. and IVA), core symptoms (Australian Scale for Asperger's Syndrome, Conners' Global Index, SNAP version of the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD, and the ADD-Q), achievement (Wide Range Achievement Test), and intelligence (Wechsler Intelligence Scales). The average gain for the Full Scale IQ score was 9 points. A decrease in relevant EEG ratios was also observed. The ratios measured were (4-8 Hz)(2)/(13-21 Hz)(2), (4-8 Hz)/(16-20 Hz), and (3-7 Hz)/(12-15 Hz). The positive outcomes of decreased symptoms of Asperger's and ADHD (including a decrease in difficulties with attention, anxiety, aprosodias, and social functioning) plus improved academic and intellectual functioning, provide preliminary support for the use of neurofeedback as a helpful component of effective intervention in people with AS.
20:46 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, neurofeedback, asperger
Sep 21, 2009
The use of biofeedback in clinical virtual reality: the intrepid project
The use of biofeedback in clinical virtual reality: the intrepid project.
Stud Health Technol Inform. 2009;144:128-32
Authors: Repetto C, Gorini A, Algeri D, Vigna C, Gaggioli A, Riva G
In our protocol for the treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorders we use Virtual reality (VR) to facilitate emotional regulation and the relaxation process. Using a biofeedback biomonitoring system (GSR, HR, Thermal) the patient is made aware of his or her reactions through the modification of some features of the VR environment in real time. Using mental exercises the patient learns to control these physiological parameters and using the feedback provided by the virtual environment is able to gauge his or her success. To test this concept, we planned a randomized controlled trial (NCT00602212), including three groups of 15 patients each (for a total of 45 patients): (1) the VR group, (2) the non-VR group, and (3) the waiting list (WL) group.
16:54 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Cybertherapy, Telepresence & virtual presence | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: virtual reality, biofeedback
Neurofeedback-based motor imagery training for brain-computer interface
Neurofeedback-based motor imagery training for brain-computer interface (BCI).
J Neurosci Methods. 2009 Apr 30;179(1):150-6
Authors: Hwang HJ, Kwon K, Im CH
In the present study, we propose a neurofeedback-based motor imagery training system for EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI). The proposed system can help individuals get the feel of motor imagery by presenting them with real-time brain activation maps on their cortex. Ten healthy participants took part in our experiment, half of whom were trained by the suggested training system and the others did not use any training. All participants in the trained group succeeded in performing motor imagery after a series of trials to activate their motor cortex without any physical movements of their limbs. To confirm the effect of the suggested system, we recorded EEG signals for the trained group around sensorimotor cortex while they were imagining either left or right hand movements according to our experimental design, before and after the motor imagery training. For the control group, we also recorded EEG signals twice without any training sessions. The participants' intentions were then classified using a time-frequency analysis technique, and the results of the trained group showed significant differences in the sensorimotor rhythms between the signals recorded before and after training. Classification accuracy was also enhanced considerably in all participants after motor imagery training, compared to the accuracy before training. On the other hand, the analysis results for the control EEG data set did not show consistent increment in both the number of meaningful time-frequency combinations and the classification accuracy, demonstrating that the suggested system can be used as a tool for training motor imagery tasks in BCI applications. Further, we expect that the motor imagery training system will be useful not only for BCI applications, but for functional brain mapping studies that utilize motor imagery tasks as well.
16:53 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Brain-computer interface, Mental practice & mental simulation | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, brain computer interface, motor imagery
Neurofeedback and brain-computer interface clinical applications
Neurofeedback and brain-computer interface clinical applications.
Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;86:107-17
Authors: Birbaumer N, Ramos Murguialday A, Weber C, Montoya P
Most of the research devoted to BMI development consists of methodological studies comparing different online mathematical algorithms, ranging from simple linear discriminant analysis (LDA) (Dornhege et al., 2007) to nonlinear artificial neural networks (ANNs) or support vector machine (SVM) classification. Single cell spiking for the reconstruction of hand movements requires different statistical solutions than electroencephalography (EEG)-rhythm classification for communication. In general, the algorithm for BMI applications is computationally simple and differences in classification accuracy between algorithms used for a particular purpose are small. Only a very limited number of clinical studies with neurological patients are available, most of them single case studies. The clinical target populations for BMI-treatment consist primarily of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and severe CNS damage including spinal cord injuries and stroke resulting in substantial deficits in communication and motor function. However, an extensive body of literature started in the 1970s using neurofeedback training. Such training implemented to control various EEG-measures provided solid evidence of positive effects in patients with otherwise pharmacologically intractable epilepsy, attention deficit disorder, and hyperactivity ADHD. More recently, the successful introduction and testing of real-time fMRI and a NIRS-BMI opened an exciting field of interest in patients with psychopathological conditions.
16:46 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Brain-computer interface | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: brain computer interface, neurofeedback
Is neurofeedback an efficacious treatment for ADHD? A randomised controlled clinical trial
Is neurofeedback an efficacious treatment for ADHD? A randomised controlled clinical trial.
J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2009 Jul;50(7):780-9
Authors: Gevensleben H, Holl B, Albrecht B, Vogel C, Schlamp D, Kratz O, Studer P, Rothenberger A, Moll GH, Heinrich H
BACKGROUND: For children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a reduction of inattention, impulsivity and hyperactivity by neurofeedback (NF) has been reported in several studies. But so far, unspecific training effects have not been adequately controlled for and/or studies do not provide sufficient statistical power. To overcome these methodological shortcomings we evaluated the clinical efficacy of neurofeedback in children with ADHD in a multisite randomised controlled study using a computerised attention skills training as a control condition. METHODS: 102 children with ADHD, aged 8 to 12 years, participated in the study. Children performed either 36 sessions of NF training or a computerised attention skills training within two blocks of about four weeks each (randomised group assignment). The combined NF treatment consisted of one block of theta/beta training and one block of slow cortical potential (SCP) training. Pre-training, intermediate and post-training assessment encompassed several behaviour rating scales (e.g., the German ADHD rating scale, FBB-HKS) completed by parents and teachers. Evaluation ('placebo') scales were applied to control for parental expectations and satisfaction with the treatment. RESULTS: For parent and teacher ratings, improvements in the NF group were superior to those of the control group. For the parent-rated FBB-HKS total score (primary outcome measure), the effect size was .60. Comparable effects were obtained for the two NF protocols (theta/beta training, SCP training). Parental attitude towards the treatment did not differ between NF and control group. CONCLUSIONS: Superiority of the combined NF training indicates clinical efficacy of NF in children with ADHD. Future studies should further address the specificity of effects and how to optimise the benefit of NF as treatment module for ADHD.
16:44 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback
Jun 24, 2009
Neurofeedback-based motor imagery training for brain-computer interface
Neurofeedback-based motor imagery training for brain-computer interface (BCI).
J Neurosci Methods. 2009 Apr 30;179(1):150-6
Authors: Hwang HJ, Kwon K, Im CH
In the present study, we propose a neurofeedback-based motor imagery training system for EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI). The proposed system can help individuals get the feel of motor imagery by presenting them with real-time brain activation maps on their cortex. Ten healthy participants took part in our experiment, half of whom were trained by the suggested training system and the others did not use any training. All participants in the trained group succeeded in performing motor imagery after a series of trials to activate their motor cortex without any physical movements of their limbs. To confirm the effect of the suggested system, we recorded EEG signals for the trained group around sensorimotor cortex while they were imagining either left or right hand movements according to our experimental design, before and after the motor imagery training. For the control group, we also recorded EEG signals twice without any training sessions. The participants' intentions were then classified using a time-frequency analysis technique, and the results of the trained group showed significant differences in the sensorimotor rhythms between the signals recorded before and after training. Classification accuracy was also enhanced considerably in all participants after motor imagery training, compared to the accuracy before training. On the other hand, the analysis results for the control EEG data set did not show consistent increment in both the number of meaningful time-frequency combinations and the classification accuracy, demonstrating that the suggested system can be used as a tool for training motor imagery tasks in BCI applications. Further, we expect that the motor imagery training system will be useful not only for BCI applications, but for functional brain mapping studies that utilize motor imagery tasks as well.
18:48 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Mental practice & mental simulation | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: mental simulation, motor imagery, rehabilitation, brain-computer interface, neurofeedback
Jun 09, 2009
Neurofeedback-based motor imagery training for brain-computer interface
Neurofeedback-based motor imagery training for brain-computer interface (BCI).
J Neurosci Methods. 2009 Apr 30;179(1):150-156
Authors: Hwang HJ, Kwon K, Im CH
In the present study, we propose a neurofeedback-based motor imagery training system for EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI). The proposed system can help individuals get the feel of motor imagery by presenting them with real-time brain activation maps on their cortex. Ten healthy participants took part in our experiment, half of whom were trained by the suggested training system and the others did not use any training. All participants in the trained group succeeded in performing motor imagery after a series of trials to activate their motor cortex without any physical movements of their limbs. To confirm the effect of the suggested system, we recorded EEG signals for the trained group around sensorimotor cortex while they were imagining either left or right hand movements according to our experimental design, before and after the motor imagery training. For the control group, we also recorded EEG signals twice without any training sessions. The participants' intentions were then classified using a time-frequency analysis technique, and the results of the trained group showed significant differences in the sensorimotor rhythms between the signals recorded before and after training. Classification accuracy was also enhanced considerably in all participants after motor imagery training, compared to the accuracy before training. On the other hand, the analysis results for the control EEG data set did not show consistent increment in both the number of meaningful time-frequency combinations and the classification accuracy, demonstrating that the suggested system can be used as a tool for training motor imagery tasks in BCI applications. Further, we expect that the motor imagery training system will be useful not only for BCI applications, but for functional brain mapping studies that utilize motor imagery tasks as well.
19:59 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback, Mental practice & mental simulation | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: brain-computer interface, neurofeedback, motor imagery
May 03, 2009
QEEG guided neurofeedback therapy in personality disorders
QEEG guided neurofeedback therapy in personality disorders: 13 case studies.
Clin EEG Neurosci. 2009 Jan;40(1):5-10
Authors: Surmeli T, Ertem A
According to DSM-IV, personality disorder constitutes a class only when personality traits are inflexible and maladaptive and cause either significant functional impairment or subjective distress. Classical treatment of choice for personality disorders has been psychotherapy and/or psychopharmacotherapy. Our study is to determine if subjects with antisocial personality disorders will benefit from quantitative EEG (qEEG) guided neurofeedback treatment. Thirteen subjects (9 male, 4 female) ranged in age from 19 to 48 years. All the subjects were free of medications and illicit drugs. We excluded subjects with other mental disorders by clinical assessment. Psychotherapy or psychopharmacotherapy or any other treatment model was not introduced to any of the subjects during or after neurofeedback treatment. For the subject who did not respond to neurofeedback, training was applied with 38 sessions of LORETA neurofeedback training without success. Evaluation measures included qEEG analysis with Nx Link data base, MMPI, T.O.V.A tests and SA-45 questionaries at baseline, and at the end of neurofeedback treatment. Lexicor qEEG signals were sampled at 128 Hz with 30 minutes-neurofeedback sessions completed between 80-120 sessions depending on the case, by Biolex neurofeedback system. At baseline and after every 20 sessions, patients were recorded with webcam during the interview. Twelve out of 13 subjects who received 80-120 sessions of neurofeedback training showed significant improvement based on SA-45 questionaries, MMPI, T.O.V.A. and qEEG/Nx Link data base (Neurometric analysis) results, and interviewing by parent/family members. Neurofeedback can change the view of psychiatrists and psychologists in the future regarding the treatment of personality disorders. This study provides the first evidence for positive effects of neurofeedback treatment in antisocial personality disorders. Further study with controls is warranted.
21:36 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, neurofeedback
Oct 22, 2008
A learning theory for reward-modulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity with application to biofeedback
A learning theory for reward-modulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity with application to biofeedback.
PLoS Comput Biol. 2008 Oct;4(10):e1000180
Authors: Legenstein R, Pecevski D, Maass W
Reward-modulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) has recently emerged as a candidate for a learning rule that could explain how behaviorally relevant adaptive changes in complex networks of spiking neurons could be achieved in a self-organizing manner through local synaptic plasticity. However, the capabilities and limitations of this learning rule could so far only be tested through computer simulations. This article provides tools for an analytic treatment of reward-modulated STDP, which allows us to predict under which conditions reward-modulated STDP will achieve a desired learning effect. These analytical results imply that neurons can learn through reward-modulated STDP to classify not only spatial but also temporal firing patterns of presynaptic neurons. They also can learn to respond to specific presynaptic firing patterns with particular spike patterns. Finally, the resulting learning theory predicts that even difficult credit-assignment problems, where it is very hard to tell which synaptic weights should be modified in order to increase the global reward for the system, can be solved in a self-organizing manner through reward-modulated STDP. This yields an explanation for a fundamental experimental result on biofeedback in monkeys by Fetz and Baker. In this experiment monkeys were rewarded for increasing the firing rate of a particular neuron in the cortex and were able to solve this extremely difficult credit assignment problem. Our model for this experiment relies on a combination of reward-modulated STDP with variable spontaneous firing activity. Hence it also provides a possible functional explanation for trial-to-trial variability, which is characteristic for cortical networks of neurons but has no analogue in currently existing artificial computing systems. In addition our model demonstrates that reward-modulated STDP can be applied to all synapses in a large recurrent neural network without endangering the stability of the network dynamics.
19:18 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback
Jul 28, 2008
Development and preliminary evaluation of a prototype audiovisual biofeedback device
Development and preliminary evaluation of a prototype audiovisual biofeedback device incorporating a patient-specific guiding waveform.
Phys Med Biol. 2008 May 12;53(11):N197-N208
Authors: Venkat RB, Sawant A, Suh Y, George R, Keall PJ
The aim of this research was to investigate the effectiveness of a novel audio-visual biofeedback respiratory training tool to reduce respiratory irregularity. The audiovisual biofeedback system acquires sample respiratory waveforms of a particular patient and computes a patient-specific waveform to guide the patient's subsequent breathing. Two visual feedback models with different displays and cognitive loads were investigated: a bar model and a wave model. The audio instructions were ascending/descending musical tones played at inhale and exhale respectively to assist in maintaining the breathing period. Free-breathing, bar model and wave model training was performed on ten volunteers for 5 min for three repeat sessions. A total of 90 respiratory waveforms were acquired. It was found that the bar model was superior to free breathing with overall rms displacement variations of 0.10 and 0.16 cm, respectively, and rms period variations of 0.77 and 0.33 s, respectively. The wave model was superior to the bar model and free breathing for all volunteers, with an overall rms displacement of 0.08 cm and rms periods of 0.2 s. The reduction in the displacement and period variations for the bar model compared with free breathing was statistically significant (p = 0.005 and 0.002, respectively); the wave model was significantly better than the bar model (p = 0.006 and 0.005, respectively). Audiovisual biofeedback with a patient-specific guiding waveform significantly reduces variations in breathing. The wave model approach reduces cycle-to-cycle variations in displacement by greater than 50% and variations in period by over 70% compared with free breathing. The planned application of this device is anatomic and functional imaging procedures and radiation therapy delivery.
13:17 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, neurofeedback
Energetic assessment of trunk postural modifications induced by a wearable audio-biofeedback system
Energetic assessment of trunk postural modifications induced by a wearable audio-biofeedback system.
Med Eng Phys. 2008 Jul 2;
Authors: Giansanti D, Dozza M, Chiari L, Maccioni G, Cappello A
13:16 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, neurofeedback
Apr 23, 2008
The effect of biofeedback training on affective regulation and simulated car-racing performance
The effect of biofeedback training on affective regulation and simulated car-racing performance: A multiple case study analysis.
J Sports Sci. 2008 May;26(7):761-73
Authors: Edmonds WA, Tenenbaum G, Mann DT, Johnson M, Kamata A
The foundation of this study was based on an idiosyncratic concept, which uses probabilistic determinations (Kamata, Tenenbaum, & Hanin, 2002) to verify the utility and effectiveness of a biofeedback intervention by manipulating affective performance states in a race-car simulator. Nine males completed five separate time-trials of a simulated racing task and were then randomly assigned to one of three arousal regulation treatment conditions: (1) optimal, (2) poor, and (3) attention control. Following the biofeedback intervention, participants underwent another series of race trials to determine the effectiveness of the arousal regulation intervention. The results indicated that there were relative similarities in the strength and direction of the perceived and physiological states between the participants; however, the subtle details of the participants' unique performance zones and the probability of achieving each zone were revealed to be unique among the participants. The results also indicated that: (a) the biofeedback manipulation resulted in the expected changes for each participant, and (b) there were some large individual differences among the participants, necessitating the idiosyncratic approach. Limitations and future directions are also addressed.
23:08 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback
Apr 11, 2008
Alpha neurofeedback improves the maintaining ability of alpha activity
Alpha neurofeedback improves the maintaining ability of alpha activity.
Neuroreport. 2008 Feb 12;19(3):315-7
Authors: Cho MK, Jang HS, Jeong SH, Jang IS, Choi BJ, Lee MG
18:29 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback, neurofeedback
Mar 03, 2008
Integrating a Portable Biofeedback Device into Clinical Practice for Patients with Anxiety Disorders
Integrating a Portable Biofeedback Device into Clinical Practice for Patients with Anxiety Disorders: Results of a Pilot Study.
Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2008 Feb 20;
Authors: Reiner R
This study examined the effectiveness of a portable Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia (RSA) biofeedback device as an adjunct to CBT in persons with anxiety disorders and other disorders associated with autonomic dysfunction attending outpatient treatment. Participants were 24 individuals attending outpatient cognitive behavioral treatment for a range of anxiety disorders. Participants were assessed over a 3 week period. Outcomes included measures of anxiety (STAI-Y), sleep disturbances (PSQI), anger (STAEI), and subjective questions about the effectiveness of the device as a treatment adjunct. Significant reductions were found for anxiety and anger and for certain sleep variables (e.g. sleep latency). There was a significant dos-effect in that those who were more compliant had significantly greater reductions in most domains including sleep, anger and trait anxiety. Overall, participants found the device more helpful than other relaxation techniques such as mediation, yoga and unassisted breathing techniques but less helpful than exercise. The most frequently endorsed side effects were dizziness (15%) and sleepiness (55%). These preliminary results suggest that portable RSA biofeedback appears to be a promising treatment adjunct for disorders of autonomic arousal and is easily integrated into treatment. Results support the need for further investigation with more rigorous experimental designs.
23:21 Posted in Biofeedback & neurofeedback | Permalink | Comments (0) | Tags: biofeedback






